Mars: the habitable planet of the future? A bold solution has just been proposed to rehabilitate her.
Earth pioneers continue to explore the Red Planet to study it and find ancient traces of life. Meanwhile, scientists around the world are wondering how to make human exploration possible, seeing their habitat.
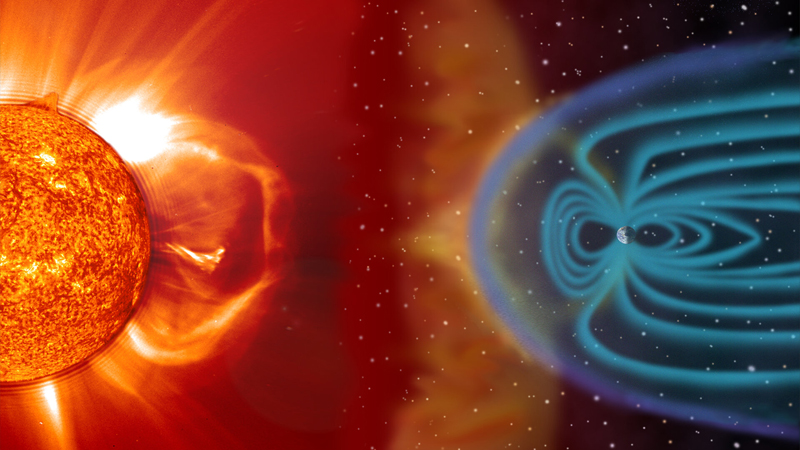
currently, Many obstacles to these ambitions stand in our way. Among them are the hostile properties of the planet.
The properties of Mars are hostile to life
- Low light levels (about 60% of Earth’s)
- Low surface gravity (38% of Earth’s)
- Sam Joe
- Atmospheric pressure (about 1% of Earth’s pressure)
- Solar and cosmic ionizing radiation at the surface
- Temperature Average temperature -63°C compared to Earth’s average of 14°C
- molecular instability
- Sand Storms
- There is no natural food source
- toxic soil
- No global magnetic field for solar wind protection
Read also> Mars was too small to sustain its oceans, lakes and rivers
reclaim Mars
Reshaping Mars is a hypothetical action consisting of a planetary engineering project or concurrent projects, with the goal of transforming Mars from a planet hostile to terrestrial life into one that can sustainably host humans and other forms of life without protection or mediation. In short, Mars made a habitable planet.
The problems are manifold and complex, of course. But at a time of increasing conquest of space, it is time to imagine solutions that may one day be within our reach.
How to create the magnetosphere on Mars
To protect itself from the solar wind and avoid a possible rapid deterioration of the atmosphere, Mars must be given an electromagnetic field.
“Earth’s magnetosphere helps protect the planet from the potentially sterilizing effects of cosmic rays and also helps maintain the atmosphere, which would otherwise be stripped away by large solar storms as they pass the planet.”
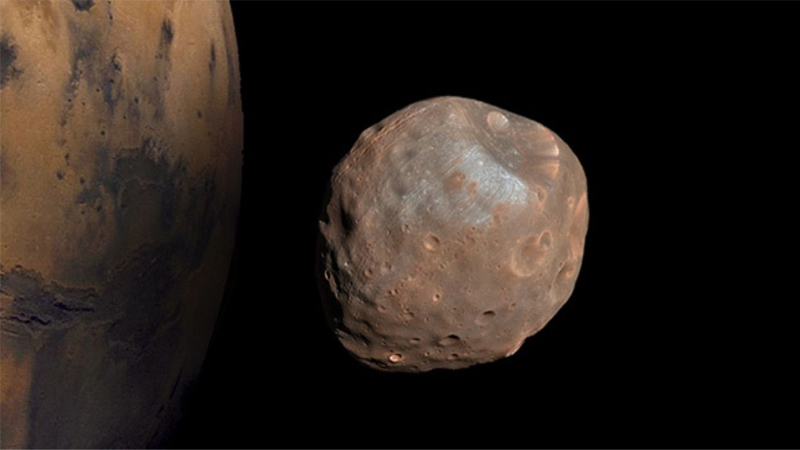

In order to create a magnetosphere strong enough to protect the developing planet Mars, a team of researchers from NASA, the RAL Space Laboratory and Princeton have proposed using Phobos, one of two satellites of the red planet. This tiny moon is so close to Mars that it orbits around it in just 8 hours. The idea is to ionize the particles on its surface, then accelerate them so that they create a plasma field that follows their orbit.
Current technological capabilities do not allow us to implement this solution in the near future. But at the rate at which things have changed since private companies have invested in the conquest of space, it is very likely that we will see a Mars rehabilitation in our lifetimes.
Read also> NASA is testing its spacesuits to (re)walk on the Moon and Mars
source : Bgr

“Unapologetic pop culture trailblazer. Freelance troublemaker. Food guru. Alcohol fanatic. Gamer. Explorer. Thinker.”



