With’technological improvement Modern humans have been able to realize one of their greatest fantasies: robots. It was originally created to help humans perform specific taskshas evolved Robots, more and more complex than ever, are asking more and more fundamental questions of man, especially those related to life. And recently, a new discovery Perhaps he laid the foundation for a new era in robotic.

new step
if for a long time, Popular culture imagined the future of robots By a certain gigantism, as we find in many works from different cultures, the real future of robotics is in the exact opposite direction, As evidenced by this new development of xenobots.
As mentioned WatchmanAnd Xenobots are artificial life forms made from cells from African clawed frog embryos (Xenopus laevis), hence their name. Thus it forms a group of a few thousand clumps of cells, It can now reproduce.
This is what was discovered recently Researchers from the University of Vermont, indicating that these xenobots can undergo A form of self-reproduction not previously seen in plants or animals. Once formed into spherical clusters about 1 millimeter in diameter, they can give rise to ‘offspring’ by dividing into free cells to form a new motile mass: “xenobot kid”.
announced in last year’s study, xenobots are what we call “living robots”. However, they have no digestive system or nerve cells, and they break down naturally after about two weeks. According to Professor Josh Bongaard, co-author of the study :
They absolutely do not turn into frogs, in fact they retain the form that we impose on them. And they look and behave completely differently compared to ordinary frogs.
Among these differences, We find in particular the process of reproduction. “You could say that anything that makes a copy of it is repeated.”Bongaard notes. But it has already been observed that plants and animals do so by reproduction. But in the review Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Bongard and colleagues show that xenobots take an entirely different approach, called motor self-repetitionAnd It is a process that has already been observed for molecules, but has never been observed for living organisms. Bongard declared:
Kinetic self-reproduction of molecules was certainly important early in life on Earth. But we don’t know if this form of repetition, which we now see in groups of cells, played a role in the origin of life.
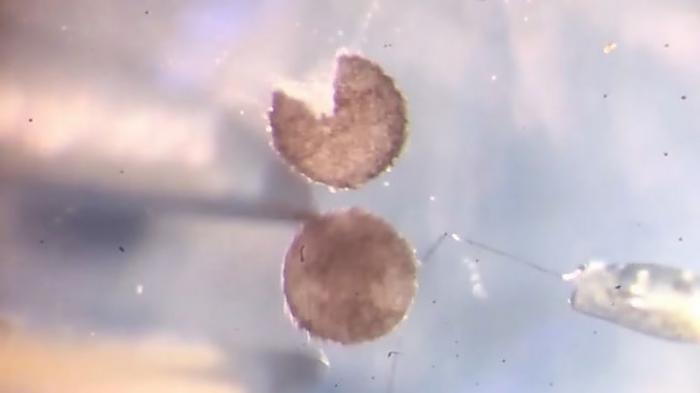
big progress
The team made their discovery by observing xenobots in Petri dishes containing room-temperature water and cells from frog embryos. Then they noticed that they could regroup and form a new mobile mass within five days, resulting in the birth of a ‘xenobot baby’. The problem is that these last two were “too young to have grandchildren”Bongaard announced. These xenobots were only able to replicate once, Not allowing another generation to be created.
But thanks to the use of artificial intelligenceThe researchers found that if the xenobots It has taken certain forms, such as the video game character Pac-ManThe repetition continued over the other generations.
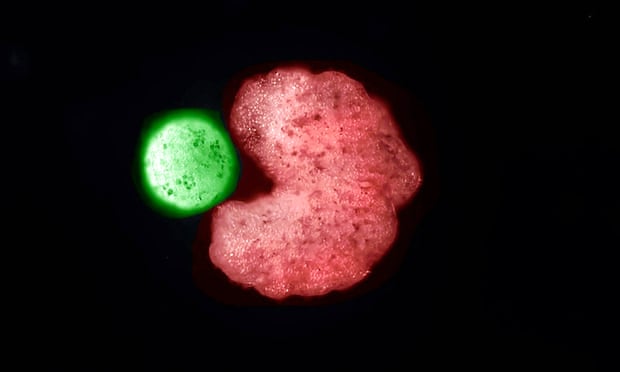
Source: The Wyss Institute
Bongard said there is hope that these self-replicating machines can eventually be developed to perform useful tasks, using computer simulations from the team. Which indicates that xenobots can repair electrical circuits. “They are very small, biodegradable, biocompatible machines, and they work well in freshwater.” He said, adding that the applications are short-term It can include the collection of microplastic particles from the streams.
In the long term, biobots made from our cells can be used in our bodies to avoid surgeries.. So it is a “Amazing science and another step towards moving materials”As stated by Professor Mark Miodonic, Director of the Institute of Manufacturing at University College London.

“Unapologetic pop culture trailblazer. Freelance troublemaker. Food guru. Alcohol fanatic. Gamer. Explorer. Thinker.”