Cases are on the rise in the country with positive rates of 1 to 30% in three weeks. There are mutations that we have not seen before and others associated in the past with greater susceptibility to transmissibility and immune evasion. UK and Israel ban flights from vulnerable African countries
The National Institute of Infectious Diseases (NICD), a division of National Health Laboratory Service (NHLS) in a South Africa, confirms that a New Covid variant identified with the initials B.1.1.529. Other labs confirm that cases are on the rise as sequencing results come in. After its disclosure, several countries – Including Italy – Banned entry from South Africa and neighboring countries.
big growth
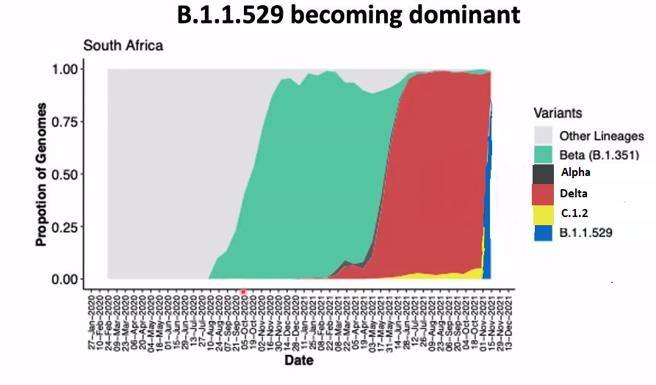
Cases detected and the percentage of positive results are increasing rapidly, particularly in Gauteng (an urban area that includes Pretoria and Johannesburg), but also in the northwest and in Limpopo. Positive rates have increased in Chuanyi (part of Guateng) in the past three weeks From less than 1% to more than 30%. Here’s how the new variant is spreading in South Africa: In the chart below (from NHLS) represents the variables spread in the country since the beginning of the epidemic. The light gray color represents the many different types of viruses that characterize the first wave; In green, the second wave is marked by beta propagation; In red the third wave of delta, in yellow the growth of states of the C.1.2 variant (still detected, but not increasing) and Blue B.1.1.529 (Increasing rapidly).
32 spikes in the spike
Variable detected Also in BotswanaIt is not known where it was born, because South Africa and Botswana (and Kenya) have better genome tracing and sequencing than other African countries.
What I know so far is that B.1.1.529 has 32 mutations in the spike protein (
The part of the virus that most vaccines use to stimulate the immune system against Covid), much more than beta and delta combined. Among others: K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493K, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H.
Some mutations have not been seen before, others are known (we know them from previous variants and previous studies) and have been linked to the variant’s ability to be more Transferable and escaping immunity by vaccinations. However, the mutations often work together, the scientists say, so it’s impossible to predict what this particular combination might mean.
It is too early to draw conclusions
The good news is that the variant can be detected by PCR tests, molecular smears, Before sequencing the genome, Thanks to the deletion of the S 69-70 gene. Laboratory studies are beginning to better understand the consequences of this alternative in relation to Transmissibility, attractiveness, and immune evasionHowever, results will take 2-3 weeks. Ravi Gupta, professor of clinical microbiology at the University of Cambridge, said work in his lab has found in the past that two mutations of mutations in B.1.1.529 led to increased infection and decreased antibody recognition.
WHO officials will (probably Friday) give the new variant a Greek name, which could be No. So far, the competition between the new variants with Delta has won over the latter due to its high portability that no other variant has been able to establish itself.
The surrogate was born from an immunocompromised patient
Meanwhile, measures related to vaccines and protective equipment will be strengthened in South Africa. The origin of the new variant is moot: South Africa has high levels of infection, but Relatively low vaccination rates (about 24%) fully vaccinated). François Balloux, Director of UCL institute of genetics Professor of computational biology atUniversity College London, in a statement published by the media center in Science, It states that the new variant may have evolved during chronic infection For an immunocompromised person, Perhaps in a patient with HIV or AIDS untreated. Scientists said the very high number of HIV cases has complicated South Africa’s efforts to combat the coronavirus pandemic, as immunocompromised people can harbor the virus for longer.
25 November 2021 (change on 26 November 2021 | 09:30)
© Reproduction reserved

“Reader. Travel maven. Student. Passionate tv junkie. Internet ninja. Twitter advocate. Web nerd. Bacon buff.”