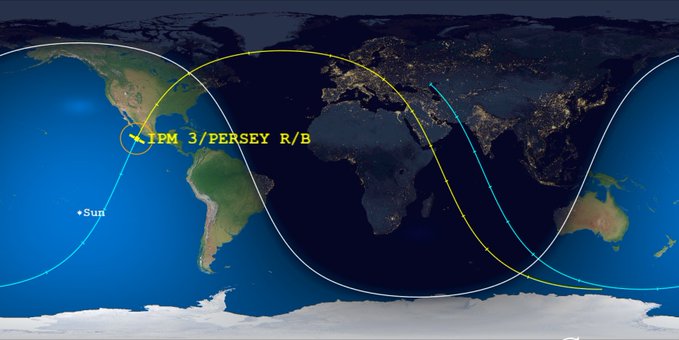
Space experts follow part of a A Russian missile fell in an uncontrolled atmosphere in the Earth’s atmosphere. heavy missile Angara-A5 It was launched from the Plesetsk Cosmodrome in Russia’s northwestern Arkhangelsk region on Monday, December 27. The launch was testing a new upper stage of the rocket, known as the Percy booster, according to state news agency TAS, citing CNN.
Most space debris burns up when it re-enters Earth’s atmosphere, but larger portions can cause damage if they land in populated areas. “It is safe to say that within the next 24 hours it will decrease, but where, no one can know, because in several hours there will be several revolutions around the worldHolger Kraj, head of the European Space Agency’s (ESA) debris office, told CNN this morning. Part of the Russian missile was traveling at 7.5 kilometers per second and its return latitude is likely to be between 63 degrees north and south of the equator, Kragh said.
The US Space Command confirmed in a statement that it “Realizes that it is tracking the location of the body of an Angara A5 / PERSEY rocket in space‘, assessment of the point of entry into the Earth’s atmosphere in the South Pacific Ocean. The return window around . is estimated 22 Italian, About an hour of uncertainty. This means that the missile should have already crashed: however, it would take hours to figure out the exact location at which it fell.
danger level
While it is highly unlikely that it will cause harm or injury to anyone, The danger is real and cannot be ignored“Happy Garage. In May 2021, NASA severely criticized China for its failure to… “Meet responsible standardsAfter the debris from an out-of-control rocket used to launch the Chinese space station fell into the Indian Ocean.
Cragg said he believes a portion of the Russian missile is smaller than the Chinese debris, weighing about 4 tons without fuel, compared to about 20 tons on the Chinese Long March 5B missile. One of the largest objects in recent memory to hit Earth was the Chinese Long March rocket after de-orbiting, after crashing in 2018, a piece of a Chinese space laboratory crashed over the Pacific Ocean and re-entered in 2020. Another Long March 5B rocket.
The Percy booster is about 10 meters long compared to the 32-meter Long March 5B rocket, said Jonathan McDowell, an astronomer at the Harvard and Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. Despite its lower weight, it carried about 16 tons of propellant on board, he said. the “The total mass is about the same as the Chinese phase, but most of it will probably be liquid and will burn in the atmosphere, so the danger to the soil is significantly less, I thinkMcDowell said.
McDowell added that the Russian missile’s stage was not intended to re-enter Earth’s atmosphere like this: “It should have ended up in an orbit where it would stay for thousands of years. The missile was unable to restart.”
The Russian space agency Roscosmos told CNN that the launch is operated by the Russian Defense Ministry.
Cragg said international best practice for parts of missiles or spacecraft at the end of their life is usually controlled re-entry and fall to land in an uninhabited area, usually a remote part of the Pacific Ocean. On average, 100 to 200 tons of space waste enter Earth’s atmosphere uncontrollably each year, Cragg added. Only one person is known to have been hit by space debris: a 1997 Texas woman named Lottie Williams, who survived.

“Reader. Travel maven. Student. Passionate tv junkie. Internet ninja. Twitter advocate. Web nerd. Bacon buff.”